找到
16
篇与
软件
相关的结果
-
 编译安装带 Brotli 压缩的 Nginx 安装依赖 apt install dpkg-dev curl gnupg2 build-essential zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev unzip cmake -y下载编译源码 添加nginx源码库 添加 Nginx 密钥: curl -L https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | apt-key add -添加密钥后,使用以下命令添加 Nginx 存储库: vim /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list添加如下内容 deb http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ focal nginx deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ focal nginx更新存储库 apt update -y 下载nginx Brotli 源文件 目录文件最好保持一致,在后续编译配置文件修改部分需要文件路径正确 cd /usr/local/src apt source nginx安装编译nginx所需要的文件 apt build-dep nginx -y从github下载 Brotli 源代码: git clone --recursive https://github.com/google/ngx_brotli.git 修改编译配置文件 修改Nginx 源并编辑 debian 规则文件添加 Brotli模块 : cd /usr/local/src/nginx-*/ vim debian/rules添加位置不同位置可能有些许不同,这里需要注意模块路径,也就是github下载 Brotli 源代码存储路径,如果位置不对需要自行修改 1.26.1版本 image-20240703160843201图片 1.22.1版本 其他版本添加位置也可能会有不同 --add-module=/usr/local/src/ngx_brotli 编译文件 使用以下命令编译并构建具有 ngx_brotli 支持的 nginx 包: dpkg-buildpackage -b -uc -us在编译时如果出现以下报错: /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lbrotlienc /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lbrotlicommon collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status make[2]: *** [objs/Makefile:383: objs/nginx] Error 1 make[2]: Leaving directory '/usr/local/src/nginx-1.26.1/debian/build-nginx' make[1]: *** [Makefile:10: build] Error 2 make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/local/src/nginx-1.26.1/debian/build-nginx' make: *** [debian/rules:62: build-arch.nginx] Error 2 dpkg-buildpackage: error: debian/rules build subprocess returned exit status 2image-20240703162706876图片 只需要编译编译一下brotli子模块即可 cd /usr/local/src/ngx_brotli/deps/brotli mkdir out cd out cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release .. makebrotli子模块编译完成后再执行编译命令 cd /usr/local/src/nginx-* dpkg-buildpackage -b -uc -us 若没有新的报错出现,在/usr/local/src就有可安装的deb软件包 安装 Nginx 并启用 Brotli 支持 安装软件包 cd /usr/local/src/ dpkg -i *.deb若软件无法安装,出现如下报错 image-20240703163851175图片 新nginx和原有的冲突,现在安装的nginx再重新安装即可 apt remove nginx apt --fix-broken install 启用Brotli 安装所有软件包后,编辑 Nginx 主配置文件并启用 Brotli 支持: vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf在 http{ 下面添加以下行 brotli on; brotli_comp_level 6; brotli_static on; brotli_types text/plain text/css application/javascript application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript image/x-icon image/vnd.microsoft.icon image/bmp image/svg+xml;重新启动 Nginx 服务: systemctl restart nginx 验证 Nginx 和 Brotli curl -H 'Accept-Encoding: br' -I http://localhost如果一切正常,您将看到 brotli 支持的结果“content-encoding:br”,如下所示: 禁用nginx更新 将 nginx 标记为保持: sudo apt-mark hold nginx查看所有被标记为“保持”的包: apt-mark showhold取消“保持”状态,允许更新: sudo apt-mark unhold nginx
编译安装带 Brotli 压缩的 Nginx 安装依赖 apt install dpkg-dev curl gnupg2 build-essential zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev unzip cmake -y下载编译源码 添加nginx源码库 添加 Nginx 密钥: curl -L https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | apt-key add -添加密钥后,使用以下命令添加 Nginx 存储库: vim /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list添加如下内容 deb http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ focal nginx deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ focal nginx更新存储库 apt update -y 下载nginx Brotli 源文件 目录文件最好保持一致,在后续编译配置文件修改部分需要文件路径正确 cd /usr/local/src apt source nginx安装编译nginx所需要的文件 apt build-dep nginx -y从github下载 Brotli 源代码: git clone --recursive https://github.com/google/ngx_brotli.git 修改编译配置文件 修改Nginx 源并编辑 debian 规则文件添加 Brotli模块 : cd /usr/local/src/nginx-*/ vim debian/rules添加位置不同位置可能有些许不同,这里需要注意模块路径,也就是github下载 Brotli 源代码存储路径,如果位置不对需要自行修改 1.26.1版本 image-20240703160843201图片 1.22.1版本 其他版本添加位置也可能会有不同 --add-module=/usr/local/src/ngx_brotli 编译文件 使用以下命令编译并构建具有 ngx_brotli 支持的 nginx 包: dpkg-buildpackage -b -uc -us在编译时如果出现以下报错: /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lbrotlienc /usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lbrotlicommon collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status make[2]: *** [objs/Makefile:383: objs/nginx] Error 1 make[2]: Leaving directory '/usr/local/src/nginx-1.26.1/debian/build-nginx' make[1]: *** [Makefile:10: build] Error 2 make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/local/src/nginx-1.26.1/debian/build-nginx' make: *** [debian/rules:62: build-arch.nginx] Error 2 dpkg-buildpackage: error: debian/rules build subprocess returned exit status 2image-20240703162706876图片 只需要编译编译一下brotli子模块即可 cd /usr/local/src/ngx_brotli/deps/brotli mkdir out cd out cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release .. makebrotli子模块编译完成后再执行编译命令 cd /usr/local/src/nginx-* dpkg-buildpackage -b -uc -us 若没有新的报错出现,在/usr/local/src就有可安装的deb软件包 安装 Nginx 并启用 Brotli 支持 安装软件包 cd /usr/local/src/ dpkg -i *.deb若软件无法安装,出现如下报错 image-20240703163851175图片 新nginx和原有的冲突,现在安装的nginx再重新安装即可 apt remove nginx apt --fix-broken install 启用Brotli 安装所有软件包后,编辑 Nginx 主配置文件并启用 Brotli 支持: vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf在 http{ 下面添加以下行 brotli on; brotli_comp_level 6; brotli_static on; brotli_types text/plain text/css application/javascript application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript image/x-icon image/vnd.microsoft.icon image/bmp image/svg+xml;重新启动 Nginx 服务: systemctl restart nginx 验证 Nginx 和 Brotli curl -H 'Accept-Encoding: br' -I http://localhost如果一切正常,您将看到 brotli 支持的结果“content-encoding:br”,如下所示: 禁用nginx更新 将 nginx 标记为保持: sudo apt-mark hold nginx查看所有被标记为“保持”的包: apt-mark showhold取消“保持”状态,允许更新: sudo apt-mark unhold nginx -
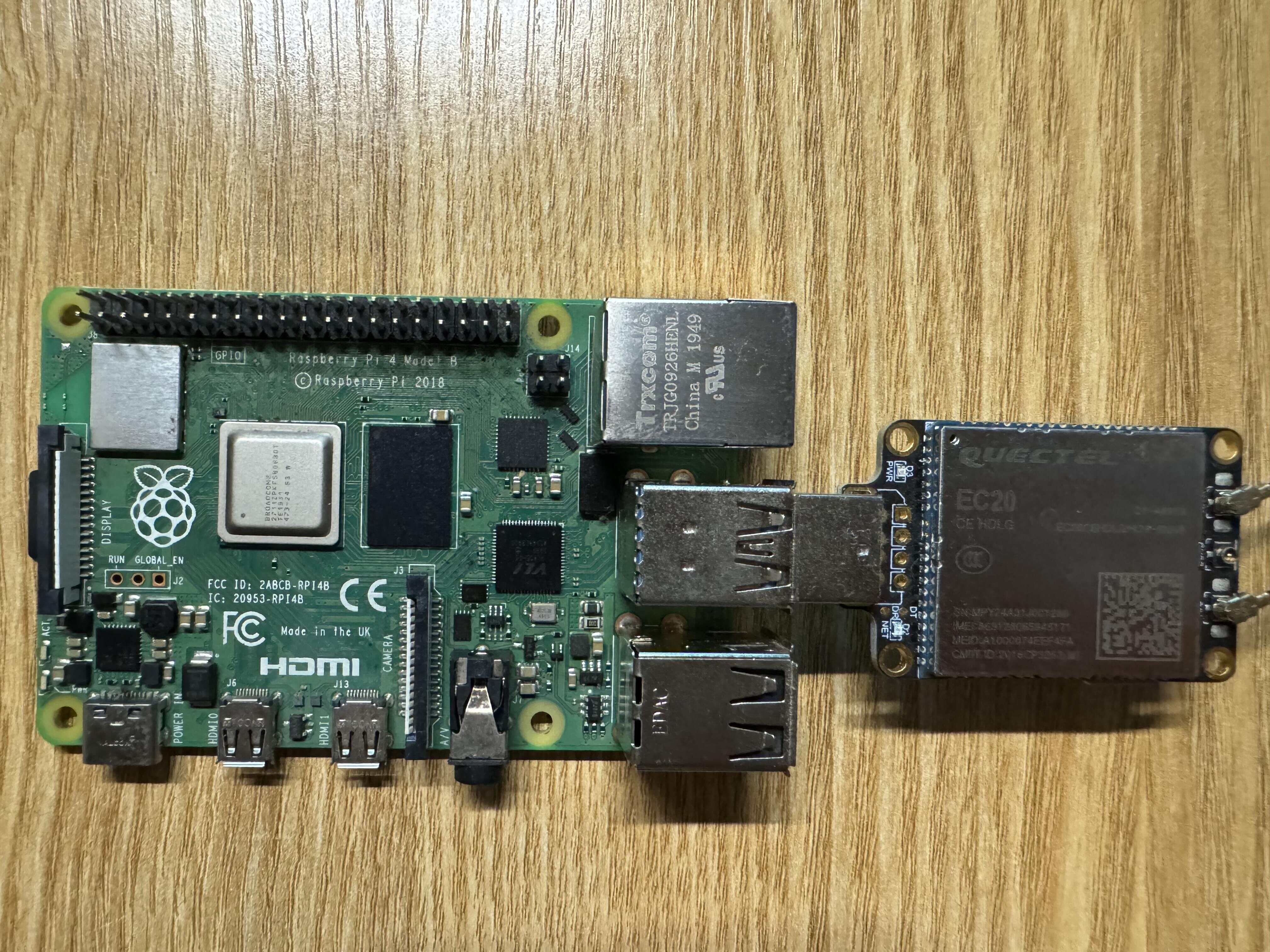
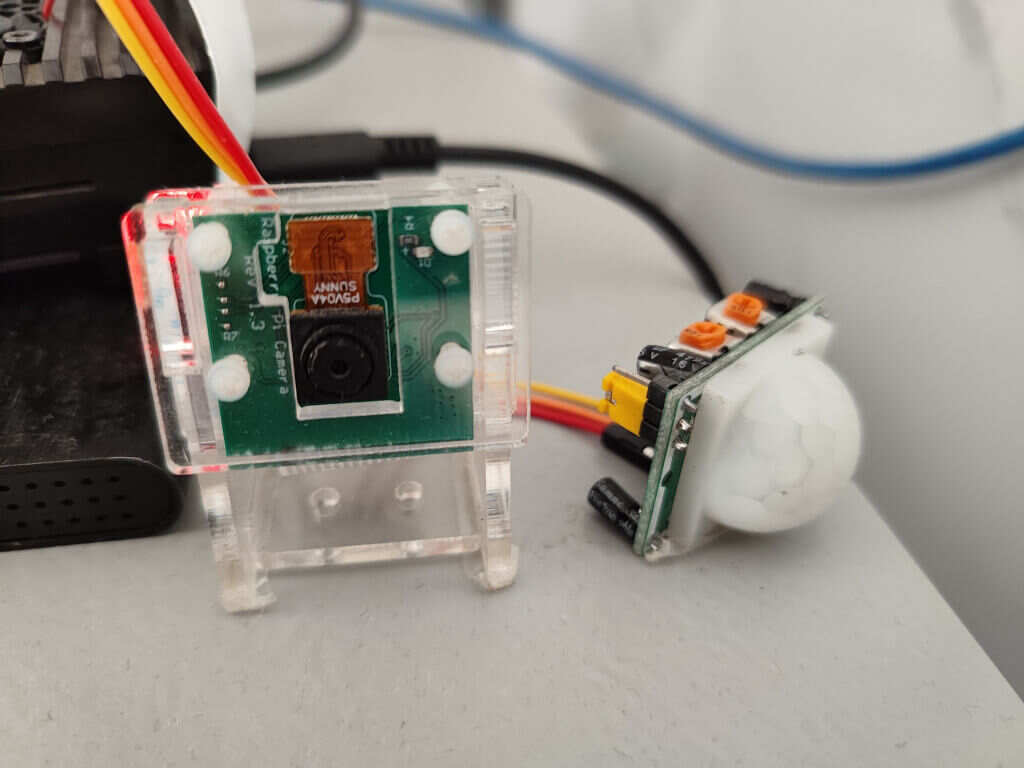
 树莓派+EC20模块实现连接蜂窝网和短信收发 软硬件 树莓派 ec20 wvdial gammu SIM卡 EC20模块 概述 EC20-CE是移远通信最近推出的LTE Cat 4无线通信模块,采用LTE 3GPP Release 11 技术,支持最大下行速率 150 Mbps和最大上行速率50 Mbps;同时在封装上兼容移远通信多网络制式LTE EC21系列、EC25系列和EG25-G 模块,实现了3G网络与4G网络之间的无缝切换。 EC20-CE采用镭雕工艺,镭雕工艺具有外观更漂亮、金属质感强、散热更好、信息不容易被抹除、更能适应自动化需求等优点。 EC20-CE内置多星座高精度定位GNSS(GPS/GLONASS/BDS/Galileo/QZSS)接收机;在简化产品设计的同时,还大大提升了定位速度及精度。 EC20-CE内置丰富的网络协议,集成多个工业标准接口,并支持多种驱动和软件功能(适用于Windows 7/8/8.1/10/11、Linux、Android等操作系统下的USB驱动等),极大地拓展了EC20-CE在M2M领域的应用范围,如CPE、路由器、数据卡、平板电脑、车载、智能安全以及工业级PDA等。 产品特性 更多详情可到官网查看 {%link LTE EC20-CE,QUECTEL,https://www.quectel.com.cn/product/lte-ec20-ce %} 产品手册 Quectel_Product_Brochure_CN_V7.8) 查看设备是否挂载成功 使用命令 sudo ls /dev |grep ttyUSB挂载成功会有如图输出 要是没有看到设备则检查设备是否稳定插入、更换USB口或者重启设备之后再重新使用命令查看 拨号上网 wvdial 安装 wvdial是一个方便使用的PPP拨号模块,它能调用调制调节器,并通过PPP上网,无需像手动拨号一样配置繁琐的文件 sudo apt update sudo apt install wvdial 配置 修改配置文件 sudo vim /etc/wvdial.conf 可以继续使用 [Dialer Defaults]也可以重新根据自己需要添加,我这里为了没有多余手机卡,也为了方便输入命令,就直接使用 电信/移动SIM卡使用以下配置 [Dialer Defaults] Init1 = ATZ Init2 = ATQ0 V1 E1 S0=0 &C1 &D2 +FCLASS=0 Modem Type = Analog Modem Modem = /dev/ttyUSB3 Baud = 115200 New PPPD = yes ISDN = 0 Phone = *99# Username = card Password = card联通卡使用以下配置 [Dialer Defaults] Init1 = ATZ Init2 = ATQ0 V1 E1 S0=0 &C1 &D2 +FCLASS=0 Init3 = at+cgdcont=1,"ip","uninet" Modem Type = Analog Modem Modem = /dev/ttyUSB3 Baud = 115200 New PPPD = yes ISDN = 0 Phone = *99# Password = card Username = card配置来源于 Quectel EC20 在 Linux 上的使用 在配置文件中大部分都不需要自己调整,只有Modem和Baud需要根据自己设备情况进行调整 Modem:根据情况选择合适的设备我的这个ttyUSB2和ttyUSB3都能正常使用 Baud:根据情况选择合适的波特率,对于ec20来说9600-115200都可以 启动wvdial sudo wvdial 查看网络设备 ifconfig 可以看到多了ppp0和wwan0两个设备 正常情况还无法访问网络,因为默认路由在其他网络设备中,需要重新配置路由 配置路由 查看路由 sudo route配置路由的方式有很多种,我这里的方法比较简单粗暴,需要具体配置的可自己查找方法 sudo route add default dev ppp0该命令会在路由表中添加一条新的默认路由 在每次重启后都会刷新路由,可以将命令加到/etc/rc.local中,每次开机都执行添加方法 sudo vim /etc/rc.local在exit 0前添加 su - root -c `route add default dev ppp0`通过systemctl来管理wvdial 开机自启wvdial的方法有很多种,并不一定要使用systemctl 最简单的就是和添加路由一样,在/etc/rc.local中添加启动命令 sudo vim /etc/rc.local # 添加 wvdial & 编写控制wvdial启动和检测wvdial运行脚本 新建sh脚本文件,可以放到你想存放的地方 我这里在root用户下/root/shell中 sudo mkdir /root/shell && cd shell # 名字可以任起 sudo vim onwvdial.shwvdial控制脚本内容 #!/bin/bash DEVICE_NAME="/dev/ttyUSB3" # 和wvdial配置设备一致 LOG_FILE="/var/log/wvdial_on.log" # 日志文件存储位置 PROCESS_NAME=(wvdial pppd) # 需检查占用软件 # 定义函数检查进程是否占用设备 check_device_usage() { local process_name=$1 local device=$2 local pids=$(pgrep -f "$process_name") if [ -z "$pids" ]; then return fi for pid in $pids; do echo "pid:$pid" local device_count=$(lsof -p "$pid" 2>/dev/null | grep -e "$device" | wc -l) if [ "$device_count" -gt 0 ]; then echo "占用设备:$device" kill $pid fi done return } function check_wvdial() { if pgrep -x "wvdial" >/dev/null; then return 0 # wvdial 进程在运行 else return 1 # wvdial 进程未运行 fi } for process in $PROCESS_NAME; do echo "进程名: $process" check_device_usage $process $DEVICE_NAME done wvdial >> "$LOG_FILE" 2>&1 & route add default dev ppp0 while true;do if ! check_wvdial;then echo "$(date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") - wvdial 进程未运行,正在重新启动..." >> "$LOG_FILE" wvdial >> "$LOG_FILE" 2>&1 & fi sleep 120 done该脚本包含功能: 停止wvdial启动前所需设备的占用 启动wvdial 添加ppp0默认路由 每120秒检测wvdial是否运行 记录启动、错误日志 设置可执行权限 sudo chmod u+x /root/shell/onwvdial.sh 编写systemctl控制文件 sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/wvdial_on.service配置文件内容如下: [Unit] Description=Safe Start Wvadil After=dev-ttyUSB3.device Requires=dev-ttyUSB3.device [Service] User=root Group=root ExecStart=/root/shell/onwvdial.sh # 路径根据自己配置修改 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target 启动服务 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start wvdial_on.service systemctl enable wvdial_on.service设置自启动后就不需要在/etc/rc.local中添加修改路由和启动wvdial命令了 配置防火墙 如果在ec20模块连接4G网络后还需要使用wifi则需要配置防火墙,不需要则不用配置 sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -o wlan0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i wlan0 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT 将防火墙规则写入文件 sudo sh -c "iptables-save > /etc/iptables.ipv4.nat"顺序执行命令即可 收发短信 安装软件gammu sudo apt install gammu gammu-smsd 配置gammu 使用命令 sudo gammu-config配置可参考我的 或者直接修改/root/.gammurc,效果是一样的 如果没有/root/.gammurc文件就使用命令 [gammu] port = /dev/ttyUSB2 model = connection = at19200 synchronizetime = yes logfile = logformat = nothing use_locking = no gammuloc =修改 /etc/gammu-smsdrc [gammu] # Please configure this! port = /dev/ttyUSB2 connection = at19200 # Debugging #logformat = textall # SMSD configuration, see gammu-smsdrc(5) [smsd] service = files logfile = syslog RunOnReceive = /root/msmtp/sh/send-smsd.sh # 发送邮件脚本 # Increase for debugging information debug = yes #debuglevel = 0 # Paths where messages are stored inboxpath = /var/spool/gammu/inbox/ outboxpath = /var/spool/gammu/outbox/ sentsmspath = /var/spool/gammu/sent/ errorsmspath = /var/spool/gammu/error/ 编辑收到短信后自动发送邮件脚本 树莓派配置邮件这里不再赘述,可以自行搜索,或者参考我之前的一篇博客 {% link 树莓派开机自动发送邮件,TeohZY,https://blog.teohzy.com/posts/smpxjfsyj/ %} 编辑脚本 vim /root/msmtp/sh/send-smsd.sh文件路径根据自己需要修改 #!/bin/bash for i in `seq $SMS_MESSAGES` ; do if [ $i -eq 1 ]; then phone="$SMS_1_NUMBER" fi tmp="$(eval echo '$'SMS_${i}_TEXT)" message="$text$tmp" done echo "$message" |mutt -s "树莓派短信转发" xxx@163.com 重启gammu systemctl restart gammu-smsd.service 短信测试 向目标号码发送短信后邮箱能收到短信 通过终端向其他号码发送短信 gammu-smsd-inject TEXT 目标号码 -text '短信内容' -unicode如果收到短信说明配置成功 短信发送失败踩坑 查看端口占用 sudo lsof /dev/ttyUSB2如果有其他进程和gammu-sms占用设备,可以使用kill命令结束非必须进程 设备波特率和wvdial重复 检查wvdial配置和gammu配置,如果wvdial已经使用了ttyUSB3和波特率115200则gammu配置中就不要再使用相同设备和波特率,可以使用ttyUSB2和波特率at19200 ModemManager占用设备 查看设备后发现有进程ModemMnana在使用设备,可以停用ModemManager 需要考虑实际使用情况来判断,在确认ModemManager确实不是必要软件后再进行操作 sudo systemctl disable ModemManager.service sudo systemctl stop ModemManager.service
树莓派+EC20模块实现连接蜂窝网和短信收发 软硬件 树莓派 ec20 wvdial gammu SIM卡 EC20模块 概述 EC20-CE是移远通信最近推出的LTE Cat 4无线通信模块,采用LTE 3GPP Release 11 技术,支持最大下行速率 150 Mbps和最大上行速率50 Mbps;同时在封装上兼容移远通信多网络制式LTE EC21系列、EC25系列和EG25-G 模块,实现了3G网络与4G网络之间的无缝切换。 EC20-CE采用镭雕工艺,镭雕工艺具有外观更漂亮、金属质感强、散热更好、信息不容易被抹除、更能适应自动化需求等优点。 EC20-CE内置多星座高精度定位GNSS(GPS/GLONASS/BDS/Galileo/QZSS)接收机;在简化产品设计的同时,还大大提升了定位速度及精度。 EC20-CE内置丰富的网络协议,集成多个工业标准接口,并支持多种驱动和软件功能(适用于Windows 7/8/8.1/10/11、Linux、Android等操作系统下的USB驱动等),极大地拓展了EC20-CE在M2M领域的应用范围,如CPE、路由器、数据卡、平板电脑、车载、智能安全以及工业级PDA等。 产品特性 更多详情可到官网查看 {%link LTE EC20-CE,QUECTEL,https://www.quectel.com.cn/product/lte-ec20-ce %} 产品手册 Quectel_Product_Brochure_CN_V7.8) 查看设备是否挂载成功 使用命令 sudo ls /dev |grep ttyUSB挂载成功会有如图输出 要是没有看到设备则检查设备是否稳定插入、更换USB口或者重启设备之后再重新使用命令查看 拨号上网 wvdial 安装 wvdial是一个方便使用的PPP拨号模块,它能调用调制调节器,并通过PPP上网,无需像手动拨号一样配置繁琐的文件 sudo apt update sudo apt install wvdial 配置 修改配置文件 sudo vim /etc/wvdial.conf 可以继续使用 [Dialer Defaults]也可以重新根据自己需要添加,我这里为了没有多余手机卡,也为了方便输入命令,就直接使用 电信/移动SIM卡使用以下配置 [Dialer Defaults] Init1 = ATZ Init2 = ATQ0 V1 E1 S0=0 &C1 &D2 +FCLASS=0 Modem Type = Analog Modem Modem = /dev/ttyUSB3 Baud = 115200 New PPPD = yes ISDN = 0 Phone = *99# Username = card Password = card联通卡使用以下配置 [Dialer Defaults] Init1 = ATZ Init2 = ATQ0 V1 E1 S0=0 &C1 &D2 +FCLASS=0 Init3 = at+cgdcont=1,"ip","uninet" Modem Type = Analog Modem Modem = /dev/ttyUSB3 Baud = 115200 New PPPD = yes ISDN = 0 Phone = *99# Password = card Username = card配置来源于 Quectel EC20 在 Linux 上的使用 在配置文件中大部分都不需要自己调整,只有Modem和Baud需要根据自己设备情况进行调整 Modem:根据情况选择合适的设备我的这个ttyUSB2和ttyUSB3都能正常使用 Baud:根据情况选择合适的波特率,对于ec20来说9600-115200都可以 启动wvdial sudo wvdial 查看网络设备 ifconfig 可以看到多了ppp0和wwan0两个设备 正常情况还无法访问网络,因为默认路由在其他网络设备中,需要重新配置路由 配置路由 查看路由 sudo route配置路由的方式有很多种,我这里的方法比较简单粗暴,需要具体配置的可自己查找方法 sudo route add default dev ppp0该命令会在路由表中添加一条新的默认路由 在每次重启后都会刷新路由,可以将命令加到/etc/rc.local中,每次开机都执行添加方法 sudo vim /etc/rc.local在exit 0前添加 su - root -c `route add default dev ppp0`通过systemctl来管理wvdial 开机自启wvdial的方法有很多种,并不一定要使用systemctl 最简单的就是和添加路由一样,在/etc/rc.local中添加启动命令 sudo vim /etc/rc.local # 添加 wvdial & 编写控制wvdial启动和检测wvdial运行脚本 新建sh脚本文件,可以放到你想存放的地方 我这里在root用户下/root/shell中 sudo mkdir /root/shell && cd shell # 名字可以任起 sudo vim onwvdial.shwvdial控制脚本内容 #!/bin/bash DEVICE_NAME="/dev/ttyUSB3" # 和wvdial配置设备一致 LOG_FILE="/var/log/wvdial_on.log" # 日志文件存储位置 PROCESS_NAME=(wvdial pppd) # 需检查占用软件 # 定义函数检查进程是否占用设备 check_device_usage() { local process_name=$1 local device=$2 local pids=$(pgrep -f "$process_name") if [ -z "$pids" ]; then return fi for pid in $pids; do echo "pid:$pid" local device_count=$(lsof -p "$pid" 2>/dev/null | grep -e "$device" | wc -l) if [ "$device_count" -gt 0 ]; then echo "占用设备:$device" kill $pid fi done return } function check_wvdial() { if pgrep -x "wvdial" >/dev/null; then return 0 # wvdial 进程在运行 else return 1 # wvdial 进程未运行 fi } for process in $PROCESS_NAME; do echo "进程名: $process" check_device_usage $process $DEVICE_NAME done wvdial >> "$LOG_FILE" 2>&1 & route add default dev ppp0 while true;do if ! check_wvdial;then echo "$(date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") - wvdial 进程未运行,正在重新启动..." >> "$LOG_FILE" wvdial >> "$LOG_FILE" 2>&1 & fi sleep 120 done该脚本包含功能: 停止wvdial启动前所需设备的占用 启动wvdial 添加ppp0默认路由 每120秒检测wvdial是否运行 记录启动、错误日志 设置可执行权限 sudo chmod u+x /root/shell/onwvdial.sh 编写systemctl控制文件 sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/wvdial_on.service配置文件内容如下: [Unit] Description=Safe Start Wvadil After=dev-ttyUSB3.device Requires=dev-ttyUSB3.device [Service] User=root Group=root ExecStart=/root/shell/onwvdial.sh # 路径根据自己配置修改 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target 启动服务 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start wvdial_on.service systemctl enable wvdial_on.service设置自启动后就不需要在/etc/rc.local中添加修改路由和启动wvdial命令了 配置防火墙 如果在ec20模块连接4G网络后还需要使用wifi则需要配置防火墙,不需要则不用配置 sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -o wlan0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i wlan0 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT 将防火墙规则写入文件 sudo sh -c "iptables-save > /etc/iptables.ipv4.nat"顺序执行命令即可 收发短信 安装软件gammu sudo apt install gammu gammu-smsd 配置gammu 使用命令 sudo gammu-config配置可参考我的 或者直接修改/root/.gammurc,效果是一样的 如果没有/root/.gammurc文件就使用命令 [gammu] port = /dev/ttyUSB2 model = connection = at19200 synchronizetime = yes logfile = logformat = nothing use_locking = no gammuloc =修改 /etc/gammu-smsdrc [gammu] # Please configure this! port = /dev/ttyUSB2 connection = at19200 # Debugging #logformat = textall # SMSD configuration, see gammu-smsdrc(5) [smsd] service = files logfile = syslog RunOnReceive = /root/msmtp/sh/send-smsd.sh # 发送邮件脚本 # Increase for debugging information debug = yes #debuglevel = 0 # Paths where messages are stored inboxpath = /var/spool/gammu/inbox/ outboxpath = /var/spool/gammu/outbox/ sentsmspath = /var/spool/gammu/sent/ errorsmspath = /var/spool/gammu/error/ 编辑收到短信后自动发送邮件脚本 树莓派配置邮件这里不再赘述,可以自行搜索,或者参考我之前的一篇博客 {% link 树莓派开机自动发送邮件,TeohZY,https://blog.teohzy.com/posts/smpxjfsyj/ %} 编辑脚本 vim /root/msmtp/sh/send-smsd.sh文件路径根据自己需要修改 #!/bin/bash for i in `seq $SMS_MESSAGES` ; do if [ $i -eq 1 ]; then phone="$SMS_1_NUMBER" fi tmp="$(eval echo '$'SMS_${i}_TEXT)" message="$text$tmp" done echo "$message" |mutt -s "树莓派短信转发" xxx@163.com 重启gammu systemctl restart gammu-smsd.service 短信测试 向目标号码发送短信后邮箱能收到短信 通过终端向其他号码发送短信 gammu-smsd-inject TEXT 目标号码 -text '短信内容' -unicode如果收到短信说明配置成功 短信发送失败踩坑 查看端口占用 sudo lsof /dev/ttyUSB2如果有其他进程和gammu-sms占用设备,可以使用kill命令结束非必须进程 设备波特率和wvdial重复 检查wvdial配置和gammu配置,如果wvdial已经使用了ttyUSB3和波特率115200则gammu配置中就不要再使用相同设备和波特率,可以使用ttyUSB2和波特率at19200 ModemManager占用设备 查看设备后发现有进程ModemMnana在使用设备,可以停用ModemManager 需要考虑实际使用情况来判断,在确认ModemManager确实不是必要软件后再进行操作 sudo systemctl disable ModemManager.service sudo systemctl stop ModemManager.service -
 树莓派访客拍照C语言版 前引 不知道因为什么原因Picamera2包调用摄像头拍照,在一个程序中达到一定次数之后就会导致系统的内存泄漏,除了重启软件没有什么好的方法来解决,但作为一个监控性质的软件,经常发生这种错误还是比较无法接受的事情。 因此决定看看能不能直接使用C语言来完成监控人员到访和录像这一系列动作 代码 代码部分十分简单 #include <pigpio.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <time.h> int pinNumber = 18; int getVideo(){ time_t timep; struct tm *p; char filePath[28]; time (&timep); p=gmtime(&timep); int hour = 8+p->tm_hour; sprintf(filePath,"%s%d%02d%02d%02d%02d%02d%s","/Disk/MyCloud/Stream/Safe/",1900+p->tm_year,1+p->tm_mon,p->tm_mday,(hour>=24)?(hour-24):hour,p->tm_min,p->tm_sec,".mp4"); char command[1000]; sprintf(command,"%s%s%s%s", "libcamera-vid -t 5000 --width 1280 --height 720 --codec libav -o ",filePath," && sudo chown www-data ",filePath); return system(command); } int main() { int value = 0; if (gpioInitialise() < 0) { printf("pigpio initialization failed\n"); return 1; } gpioSetMode(pinNumber, PI_INPUT); while(1){ value = gpioRead(pinNumber); if(value==1){ getVideo(); } time_sleep(1.0); } gpioTerminate(); return 0; }由于在之前 使用的GPIO库wiringPi.h已经暂停维护,在新版的树莓派系统中不在默认安装,这里使用了pigpio.h库 如果没有安装 sudo apt update sudo apt install pigpio 编译 gcc monitor.c -o monitor -lpigpio -lrt -lpthread 引脚编号 默认为BCM编号 主要拍照代码 system(command)实际是为了调用系统的libcamera-vid 即 sprintf(command,"%s%s%s%s", "libcamera-vid -t 5000 --codec libav -o ",filePath," && sudo chown www-data ",filePath);这部分代码为录一个5秒的视频并保存到filePath目录下,同时修改视频权限方便给Nextcloud修改查看 人体红外代码 int value = 0; if (gpioInitialise() < 0) { printf("pigpio initialization failed\n"); return 1; } gpioSetMode(pinNumber, PI_INPUT); while(1){ value = gpioRead(pinNumber); if(value==1){ getVideo(); } time_sleep(1.0); } gpioTerminate();当有人到访时输出高电平,检测到高电平时触发录像
树莓派访客拍照C语言版 前引 不知道因为什么原因Picamera2包调用摄像头拍照,在一个程序中达到一定次数之后就会导致系统的内存泄漏,除了重启软件没有什么好的方法来解决,但作为一个监控性质的软件,经常发生这种错误还是比较无法接受的事情。 因此决定看看能不能直接使用C语言来完成监控人员到访和录像这一系列动作 代码 代码部分十分简单 #include <pigpio.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <time.h> int pinNumber = 18; int getVideo(){ time_t timep; struct tm *p; char filePath[28]; time (&timep); p=gmtime(&timep); int hour = 8+p->tm_hour; sprintf(filePath,"%s%d%02d%02d%02d%02d%02d%s","/Disk/MyCloud/Stream/Safe/",1900+p->tm_year,1+p->tm_mon,p->tm_mday,(hour>=24)?(hour-24):hour,p->tm_min,p->tm_sec,".mp4"); char command[1000]; sprintf(command,"%s%s%s%s", "libcamera-vid -t 5000 --width 1280 --height 720 --codec libav -o ",filePath," && sudo chown www-data ",filePath); return system(command); } int main() { int value = 0; if (gpioInitialise() < 0) { printf("pigpio initialization failed\n"); return 1; } gpioSetMode(pinNumber, PI_INPUT); while(1){ value = gpioRead(pinNumber); if(value==1){ getVideo(); } time_sleep(1.0); } gpioTerminate(); return 0; }由于在之前 使用的GPIO库wiringPi.h已经暂停维护,在新版的树莓派系统中不在默认安装,这里使用了pigpio.h库 如果没有安装 sudo apt update sudo apt install pigpio 编译 gcc monitor.c -o monitor -lpigpio -lrt -lpthread 引脚编号 默认为BCM编号 主要拍照代码 system(command)实际是为了调用系统的libcamera-vid 即 sprintf(command,"%s%s%s%s", "libcamera-vid -t 5000 --codec libav -o ",filePath," && sudo chown www-data ",filePath);这部分代码为录一个5秒的视频并保存到filePath目录下,同时修改视频权限方便给Nextcloud修改查看 人体红外代码 int value = 0; if (gpioInitialise() < 0) { printf("pigpio initialization failed\n"); return 1; } gpioSetMode(pinNumber, PI_INPUT); while(1){ value = gpioRead(pinNumber); if(value==1){ getVideo(); } time_sleep(1.0); } gpioTerminate();当有人到访时输出高电平,检测到高电平时触发录像 -
 远程访问本地搭建的NextCloud(反向代理网页) 前言 在没有公网IP的情况下,很难从其他网络环境中直接访问到部署在本地的web服务,这时候就需要通过内网穿透的方式来实现。而对于内网穿透,有着很多的实现方式,最为常见的就是通过云服务器搭建和使用别人提供的服务 自建内网穿透服务 需要有自己的云服务器 服务端和客户端都需要下载frp,下载地址 => Releases · fatedier/frp (github.com) 服务端配置 编辑frps.ini文件 [common] # frp监听的端口,默认是7000,可以改成其他的 bind_port = 7000 # 授权码,需要与客户端一致,请改为更复杂的 token = aaaaaa # frp管理后台端口,请按自己需求更改 dashboard_port = 7500 # frp管理后台用户名和密码,请改成自己的 dashboard_user = Mango dashboard_pwd = 12345678 enable_prometheus = true # http 端口可更改 vhost_http_port = 8090 # https 端口可更改 vhost_https_port= 8081 #vhost_https_port = 8080 # frp日志配置 路径根据自己需求更改 log_file = /root/frp/.frps.log log_level = error log_max_days = 3 配置systemd守护进程便于管理 vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service输入以下内容并保存 [Unit] Description=fraps service After=network.target syslog.target Wants=network.target [Service] Type=simple #启动服务的命令(此处写你的frps的实际安装目录) ExecStart=/root/frp/frps -c /root/frp/frps.ini [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target启动frps并设置开机自启 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start frps systemctl enable frps 配置nginx 如果没有nginx先安装 apt update apt install nginx编辑配置文件 vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nextcloud # 也可以不新建nextcloud文件,直接配置默认文件 vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultnginx代理frps配置文件参考 可配置SSL开启https server{ listen 80; listen 443 ssl; #对应你的域名 server_name xxx.xxx.cn; # https 域名证书相关配置 # ssl证书存储路径,根据个人存储路径设置,我的被存在了 /etc/nginx/ssl/ 文件夹下面 ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/xxx.mstzf.cn.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/xxx.mstzf.cn.key; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!RC4:!DHE; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8090; # 映射的frp服务端frps.ini的 vhost_http_port端口 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_max_temp_file_size 0; proxy_redirect off; proxy_read_timeout 240s; client_max_body_size 0; } } }重启nginx服务 systemctl restart nginx 客户端配置 编辑frpc.ini文件 [common] # 远程服务器地址 # 替换为自己的域名 server_addr = 0.0.0.0 # 远程服务器监听端口 # 和服务端 bind_port 相同 server_port = 7000 # 连接密钥 # 必须和服务端配置相同 token = aaaaaa # 配置日志文件 # 日志级别:trace, debug, info, warn, error # 日志保存路径根据需求修改 log_file = /home/zh/frp/log/.log log_level = error log_max_days = 3 # 客户端管理配置 admin_addr = 127.0.0.1 admin_port = 7500 admin_user = Mango admin_pwd = 12345678 # 代理端口配置 模板 # [内容随意 如ssh] # type = 连接类型 如 tcp # local_ip = 127.0.0.1 # local_port = 22 本地需要代理的端口 # remote_port = 2222 将本地22端口代理为远程的2222端口 # 该配置下,可用远程 ip 的 2222 端口访问到本地的 22 端口服务 [ssh] type = tcp local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port = 22 remote_port = 2222 [rdp] type=tcp local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port=3389 remote_port=3389 [nx] type=tcp local_ip=127.0.0.1 local_port=4000 remote_port=4000 [web] type = http local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port = 80 #subdomain = root # 绑定的域名 和nginx配置下的 server_name 相同 custom_domains = xxx.mstzf.cn 为frpc配置systemd守护进程便于管理 编辑文件 vim /etc/systemd/system/frpc.service输入以下内容 [Unit] Description=Frp Client Service After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=root Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5s # 根据frp所在位置设置 ExecStart=/home/zh/frp/frpc -c /home/zh/frp/frpc.ini LimitNOFILE=1048576 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target启动frpc并配置开机自启 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start frpc systemctl enable frpc 使用第三方服务 我个人使用的是Sakura Frp,有能够满足基本需求的免费套餐,vip套餐也很划算,已经能够满足我的基本需求 {% link SakuraFrp,SakuraFrp,https://www.natfrp.com/ %} 注册账号 完善个人信息 如果有建站需求想要使用国内站点,需要完成实名认证和有备案域名,否则只能使用国外的站点来搭建 在客户端安装frp软件 这一部分官网中已经介绍得十分的详细,这里只有几个关键命令,具体可到官网查看 {% link frpc 基本使用指南,SakuraFrp 帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/usage.html %} 确认系统架构 uname -m获取软件链接 {% link 软件下载,SakuraFrp,https://www.natfrp.com/tunnel/download %} 安装 cd /usr/local/bin wget -O frpc <下载地址> chmod 755 frpc 配置守护进程(systemd) 具体操作可去指导文档查看 {% link Systemd配置frpc服务,SakuraFrp帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/service/systemd.html %} 添加工作目录 mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/natfrp编辑配置文件 vim /etc/systemd/system/frpc@.service输入配置内容 [Unit] Description=SakuraFrp Service After=network.target [Service] Type=idle #DynamicUser=yes Restart=on-failure RestartSec=60s ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/frpc -f %i WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/etc/natfrp [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target重载systemd systemctl daemon-reload 新建隧道 对于远程访问网页的,需要选择可建站的节点;至于选择国内还是国外要先看自己的域名是否已经备过案,备案过的域名可以使用国内节点,国内节点在各方面都要优于国外。如果没有备案域名,就只能使用国外节点。 image-20231114121753361图片 image-20231114121907030图片 端口根据本地网页端口配置 在绑定域名和自动HTTPS中一定要输入自己需要使用的域名 配置DSN解析 动画图片 复制节点域名,到域名服务商处配置DNS解析,将自己的域名CNAME到复制的节点域名上 记录类型选择CNAME 记录值选择选择节点所绑定域名 配置SSL证书 {% link 配置frpc使用的SSL证书,SakuraFrp帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/ssl.html %} 从服务商下载域名SSL证书选择Nginx,将证书重命名为 将其中 扩展名为pem的直接将扩展名修改为crt 并只保留域名和扩展名 即 如 nextcloud.mstzf.cn.key 的形式 将证书移动到之前配置的工作目录中 /usr/local/etc/natfrp 启动隧道 systemctl <start|stop> <Unit名称> # <Unit名称> 即下图 -f 之后 红色框部分
远程访问本地搭建的NextCloud(反向代理网页) 前言 在没有公网IP的情况下,很难从其他网络环境中直接访问到部署在本地的web服务,这时候就需要通过内网穿透的方式来实现。而对于内网穿透,有着很多的实现方式,最为常见的就是通过云服务器搭建和使用别人提供的服务 自建内网穿透服务 需要有自己的云服务器 服务端和客户端都需要下载frp,下载地址 => Releases · fatedier/frp (github.com) 服务端配置 编辑frps.ini文件 [common] # frp监听的端口,默认是7000,可以改成其他的 bind_port = 7000 # 授权码,需要与客户端一致,请改为更复杂的 token = aaaaaa # frp管理后台端口,请按自己需求更改 dashboard_port = 7500 # frp管理后台用户名和密码,请改成自己的 dashboard_user = Mango dashboard_pwd = 12345678 enable_prometheus = true # http 端口可更改 vhost_http_port = 8090 # https 端口可更改 vhost_https_port= 8081 #vhost_https_port = 8080 # frp日志配置 路径根据自己需求更改 log_file = /root/frp/.frps.log log_level = error log_max_days = 3 配置systemd守护进程便于管理 vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service输入以下内容并保存 [Unit] Description=fraps service After=network.target syslog.target Wants=network.target [Service] Type=simple #启动服务的命令(此处写你的frps的实际安装目录) ExecStart=/root/frp/frps -c /root/frp/frps.ini [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target启动frps并设置开机自启 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start frps systemctl enable frps 配置nginx 如果没有nginx先安装 apt update apt install nginx编辑配置文件 vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nextcloud # 也可以不新建nextcloud文件,直接配置默认文件 vim /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultnginx代理frps配置文件参考 可配置SSL开启https server{ listen 80; listen 443 ssl; #对应你的域名 server_name xxx.xxx.cn; # https 域名证书相关配置 # ssl证书存储路径,根据个人存储路径设置,我的被存在了 /etc/nginx/ssl/ 文件夹下面 ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/xxx.mstzf.cn.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/xxx.mstzf.cn.key; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!RC4:!DHE; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8090; # 映射的frp服务端frps.ini的 vhost_http_port端口 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_max_temp_file_size 0; proxy_redirect off; proxy_read_timeout 240s; client_max_body_size 0; } } }重启nginx服务 systemctl restart nginx 客户端配置 编辑frpc.ini文件 [common] # 远程服务器地址 # 替换为自己的域名 server_addr = 0.0.0.0 # 远程服务器监听端口 # 和服务端 bind_port 相同 server_port = 7000 # 连接密钥 # 必须和服务端配置相同 token = aaaaaa # 配置日志文件 # 日志级别:trace, debug, info, warn, error # 日志保存路径根据需求修改 log_file = /home/zh/frp/log/.log log_level = error log_max_days = 3 # 客户端管理配置 admin_addr = 127.0.0.1 admin_port = 7500 admin_user = Mango admin_pwd = 12345678 # 代理端口配置 模板 # [内容随意 如ssh] # type = 连接类型 如 tcp # local_ip = 127.0.0.1 # local_port = 22 本地需要代理的端口 # remote_port = 2222 将本地22端口代理为远程的2222端口 # 该配置下,可用远程 ip 的 2222 端口访问到本地的 22 端口服务 [ssh] type = tcp local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port = 22 remote_port = 2222 [rdp] type=tcp local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port=3389 remote_port=3389 [nx] type=tcp local_ip=127.0.0.1 local_port=4000 remote_port=4000 [web] type = http local_ip = 127.0.0.1 local_port = 80 #subdomain = root # 绑定的域名 和nginx配置下的 server_name 相同 custom_domains = xxx.mstzf.cn 为frpc配置systemd守护进程便于管理 编辑文件 vim /etc/systemd/system/frpc.service输入以下内容 [Unit] Description=Frp Client Service After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=root Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5s # 根据frp所在位置设置 ExecStart=/home/zh/frp/frpc -c /home/zh/frp/frpc.ini LimitNOFILE=1048576 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target启动frpc并配置开机自启 systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start frpc systemctl enable frpc 使用第三方服务 我个人使用的是Sakura Frp,有能够满足基本需求的免费套餐,vip套餐也很划算,已经能够满足我的基本需求 {% link SakuraFrp,SakuraFrp,https://www.natfrp.com/ %} 注册账号 完善个人信息 如果有建站需求想要使用国内站点,需要完成实名认证和有备案域名,否则只能使用国外的站点来搭建 在客户端安装frp软件 这一部分官网中已经介绍得十分的详细,这里只有几个关键命令,具体可到官网查看 {% link frpc 基本使用指南,SakuraFrp 帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/usage.html %} 确认系统架构 uname -m获取软件链接 {% link 软件下载,SakuraFrp,https://www.natfrp.com/tunnel/download %} 安装 cd /usr/local/bin wget -O frpc <下载地址> chmod 755 frpc 配置守护进程(systemd) 具体操作可去指导文档查看 {% link Systemd配置frpc服务,SakuraFrp帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/service/systemd.html %} 添加工作目录 mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/natfrp编辑配置文件 vim /etc/systemd/system/frpc@.service输入配置内容 [Unit] Description=SakuraFrp Service After=network.target [Service] Type=idle #DynamicUser=yes Restart=on-failure RestartSec=60s ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/frpc -f %i WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/etc/natfrp [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target重载systemd systemctl daemon-reload 新建隧道 对于远程访问网页的,需要选择可建站的节点;至于选择国内还是国外要先看自己的域名是否已经备过案,备案过的域名可以使用国内节点,国内节点在各方面都要优于国外。如果没有备案域名,就只能使用国外节点。 image-20231114121753361图片 image-20231114121907030图片 端口根据本地网页端口配置 在绑定域名和自动HTTPS中一定要输入自己需要使用的域名 配置DSN解析 动画图片 复制节点域名,到域名服务商处配置DNS解析,将自己的域名CNAME到复制的节点域名上 记录类型选择CNAME 记录值选择选择节点所绑定域名 配置SSL证书 {% link 配置frpc使用的SSL证书,SakuraFrp帮助文档,https://doc.natfrp.com/frpc/ssl.html %} 从服务商下载域名SSL证书选择Nginx,将证书重命名为 将其中 扩展名为pem的直接将扩展名修改为crt 并只保留域名和扩展名 即 如 nextcloud.mstzf.cn.key 的形式 将证书移动到之前配置的工作目录中 /usr/local/etc/natfrp 启动隧道 systemctl <start|stop> <Unit名称> # <Unit名称> 即下图 -f 之后 红色框部分 -
 SSM开发环境搭建(小白自用) 前言 将SSM作为后端的的一个项目即将完工,在开发过程中踩了很多坑,与此同时也学习到了新知识,有了不小收获。在遇到麻烦和解决麻烦的路上,受到了很多分享教程博主的帮助。为了将帮助延续下去,我也将自己SSM环境配置的过程做了简单的纪录、分享。 系统软件版本 Windows 10 专业版 22H2 IntelliJ IDEA 2022.3.3 MySQL 8.0.32 Java 19.0.2 Spring 6.0.6 MyBatis 3.5.13 Tomcat 11.0.0 (软件系统版本不用完全一致,不同版本之间可能会出现一定程度的兼容性问题,可在有问题时在寻找对应版本的解决办法) 新建项目及项目配置 新建项目 使用IDEA新建一个空的默认Maven项目,并新建Java包完善SSM项目架构。 在新建controller包(表现层)、dao包(持久层)、service包(业务层) 在resources下新建db(存放数据库相关配置文件)、log(存放日志相关配置文件)、spring(存放与spring与其他整合相关配置文件) image-20230507141558542图片 修改Maven配置文件 使用默认Maven配置文件,在下载包时会比较慢,我们可以修改配置文件使用国内镜像来加速下载 IDEA内修改路径为File->Settings->Builde,Execution,Deployment->Maven 可以修改默认的文件,也可以重新使用一个自定义的配置文件,笔者这里使用了重新新建一个配置文件的方法。 image-20230507142114670图片 其中settings.xml文件中内容如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: | | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml | | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven | users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven | installation). It's normally provided in | ${maven.conf}/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml | | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. | |--> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.2.0.xsd"> <!-- localRepository | The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts. | | Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository <localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository> --> <!-- interactiveMode | This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, | maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for | the parameter in question. | | Default: true <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> --> <!-- offline | Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. | This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. | | Default: false <offline>false</offline> --> <!-- pluginGroups | This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e. | when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers | "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list. |--> <pluginGroups> <!-- pluginGroup | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> --> </pluginGroups> <!-- proxies | This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. | Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy | specification in this list marked as active will be used. |--> <proxies> <!-- proxy | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. | <proxy> <id>optional</id> <active>true</active> <protocol>http</protocol> <username>proxyuser</username> <password>proxypass</password> <host>proxy.host.net</host> <port>80</port> <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> </proxy> --> </proxies> <!-- servers | This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. | Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. |--> <servers> <!-- server | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by | a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below). | | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are | used together. | <server> <id>deploymentRepo</id> <username>repouser</username> <password>repopwd</password> </server> --> <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. <server> <id>siteServer</id> <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> </server> --> </servers> <!-- mirrors | This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories. | | It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts. | However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored | it to several places. | | That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that | repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred | server for that repository. |--> <mirrors> <!-- mirror | Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that | this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used | for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors. | <mirror> <id>mirrorId</id> <mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf> <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> <url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url> </mirror> --> <mirror> <id>aliment</id> <name>aliyah maven</name> <url>https://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> <mirror> <id>uk</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> <url>https://uk.maven.org/maven2/</url> </mirror> <mirror> <id>CN</id> <name>OSChina Central</name> <url>https://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> <mirror> <id>nexus</id> <name>internal nexus repository</name> <!-- <url>http://192.168.1.100:8081/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>--> <url>https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> </mirrors> <!-- profiles | This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify | the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- | specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. | | For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where | your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is | dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin. | | As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles | section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially | relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property, | or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a | value of '1.4' might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of '1.4.2_07'. | Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line. | | NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact | repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration | variables for plugins in the POM. | |--> <profiles> <!-- profile | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. | | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention | for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc. | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug. | | This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo. <profile> <id>jdk-1.4</id> <activation> <jdk>1.4</jdk> </activation> <repositories> <repository> <id>jdk14</id> <name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name> <url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url> <layout>default</layout> <snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy> </repository> </repositories> </profile> --> <!-- | Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev', | which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration | might hypothetically look like: | | ... | <plugin> | <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId> | <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId> | | <configuration> | <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation> | </configuration> | </plugin> | ... | | NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to | anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property. | <profile> <id>env-dev</id> <activation> <property> <name>target-env</name> <value>dev</value> </property> </activation> <properties> <tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath> </properties> </profile> --> </profiles> <!-- activeProfiles | List of profiles that are active for all builds. | <activeProfiles> <activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> <activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> </activeProfiles> --> </settings> 只是修改了mirrors部分,使用了阿里云镜像加速国内下载速度。 设置项目所需包 修改pom.xml文件,以下内容为本人使用成功的配置文件内容,仅作参考 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.mango</groupId> <artifactId>ssmTest</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <!-- 工程编译版本,一般与安装的JDK版本一致--> <maven.compiler.source>19</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>19</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <!--统一的版本管理--> <spring.version>6.0.6</spring.version> <slf4j.version>2.0.5</slf4j.version> <mysql.version>8.0.32</mysql.version> <mybatis.version>3.5.13</mybatis.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.19</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!--Junit--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <!--数据库驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${mysql.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>c3p0</groupId> <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> <version>0.9.1.2</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <!--Servlet - JSP --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>jstl</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <!-- @Resource注解依赖包--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <!--Mybatis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>${mybatis.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合ORM --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>6.0.6</version> </dependency> <!-- spring整合mybatis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>3.0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- log --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>2.20.0</version> <type>pom</type> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <!--加入对json转换--> <!-- JSON: jackson --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.jr</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-jr-all</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>2.0.25</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.16</version> </dependency> <!-- http请求--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> <version>3.0.4</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> </resource> </resources> </build> </project> 添加Web模块 File->Project Structure->Modules 如图操作 image-20230507143328815图片 添加后内容保持默认,确认后即可导入web模块 安装Tomcat 可以参考以下教程 {% link Wxy1122.,[IntelliJ IDEA中配置Tomcat(超详细)_idea配置tomcat_Wxy1122.的博客-CSDN博客,https://blog.csdn.net/Wxy971122/article/details/123508532 %} SSM配置文件 jdbc配置文件 在resources->db下新建jdbc.properties文件,其中内容参考如下 jdbc.driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = root由于使用的MySQL版本为8,所以驱动才使用为com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,由于没有在MySQL中做过测试,不能确定在MySQL 5中也能正常使用 jdbc.url中的xxx用自己数据库名称替换 新建mybatis控制文件 在db下新建mybatis.xml文件 由于大部分和MyBatis相关配置文件都会和Spring的配置文件整合到一起,这里的Mybatis控制文件只起到辅助作用,参考代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 开启延迟加载 该项默认为false,即所有关联属性都会在初始化时加载 true表示延迟按需加载 --> <settings> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 开启二级缓存 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings> </configuration> Spring整合MyBatis 在resources->spring下新建applicationContext.xml文件,将Spring和MyBatis配置文件整合在一起,参考代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!-- 开启注解扫描,要扫描的是service和dao层的注解,要忽略web层注解,因为web层让SpringMVC框架去管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango"> <!-- 配置要忽略的注解 --> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> <!-- 引入配置文件 --> <bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:db/jdbc.properties" /> </bean> <!--Spring整合Mybatisl框架--> <!-- 配置C3P0的连接池对象 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置SessionFactory的Bean --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- 注入数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 指定MyBatis配置文件的位置 --> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:db/mybatis.xml"/> <!-- 给实体类起别名 --> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.mango.entity"/> </bean> <!-- 配置mapper接口的扫描器,将Mapper接口的实现类自动注入到IoC容器中 实现类Bean的名称默认为接口类名的首字母小写 --> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <!-- basePackage属性指定自动扫描mapper接口所在的包 --> <property name="basePackage" value="com.mango.dao"/> </bean> <!--SqlMapConfig.xml和jdbcConfig.properties可以删除了--> <!--配置Spring框架声明式事务管理--> <!--配置事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务的通知 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="*" isolation="DEFAULT"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置AOP增强 --> <aop:config> <!-- <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.mango.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>--> <!-- 配置切入点表达式 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.mango.service.impl.*.*(..))" id="pt1"/> <!-- 建立通知和切入点表达式的关系 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"/> </aop:config> </beans> Springmvc配置文件 在resources->spring下新建springmvc.xml文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 配置@controller扫描包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango.controller" /> <!--使用Annotation自动注册Bean,扫描@Controller和@ControllerAdvice--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango" use-default-filters="false"> <!-- base-package 如果多个,用“,”分隔 --> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> <!--控制器增强,使一个Controller成为全局的异常处理类,类中用@ExceptionHandler方法注解的方法可以处理所有Controller发生的异常--> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice" /> </context:component-scan> <!-- 配置注解驱动,相当于同时使用最新处理器映射跟处理器适配器,对json数据响应提供支持 --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <!-- 输出对象转JSON支持 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="messageConverters"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"> <property name="supportedMediaTypes"> <list> <value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>text/plain;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value> </list> </property> </bean> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans> web模块控制文件 编辑web->WEB-INF->web.xml文件,内容如下 <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <!-- 配置前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- 指定配置文件位置和名称 如果不设置,默认找/WEB-INF/<servlet-name>-servlet.xml --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- 配置 spring 提供的监听器,用于启动服务时加载容器 。 该监听器只能加载 WEB-INF 目录中名称为 applicationContext.xml 的配置文件 --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 手动指定 spring 配置文件位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> </web-app> 日志配置 在resources->log下新建log4j.properties log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p %d %C: %m%n log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=INFO log4j.logger.org.apache=INFO log4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG 测试 在test->java下更具需求新建测试类 新建测试数据库test,其中有表student(id,name,age) 在之前新建的entity包中新建Student的实现类(getter、setter方法以省略) package com.mango.entity; public class Student { private int id; private String name; private String age; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age='" + age + '\'' + '}'; } } 对Spring和MyBatis整合配置测试 在包dao中新建学生接口StudentDao.java package com.mango.dao; import com.mango.entity.Student; import java.util.List; public interface StudentDao { public List<Student> findAll(); }在同样位置新建同名mapper文件StudentDao.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--命名空间为StudentDao接口--> <mapper namespace="com.mango.dao.StudentDao"> <!-- id为接口中的方法名--> <select id="findAll">SELECT * FROM Student</select> </mapper>在service包中新建service接口和实现类 image-20230507154913975图片 学生业务层接口StudentService.java package com.mango.service; import com.mango.entity.Student; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; //千万不要忘记添加Service注解 @Service public interface StudentService { public List<Student> findAll(); }实现类StudentServiceImpl.java package com.mango.service.impl; import com.mango.dao.StudentDao; import com.mango.entity.Student; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; public List<Student> findAll(){ return studentDao.findAll(); } }在test中新建Spring和MyBatis整合测试代码SpringMyBatis.java import com.mango.entity.Student; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml") public class SpringMyBatis { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @Test public void test(){ List<Student> studentList=studentService.findAll(); for (Student student:studentList){ System.out.println(student.toString()); } } } image-20230507161529932图片 测试成功 Spring整合SpringMVC测试 在Controller包中新建StudentController.java package com.mango.controller; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; //千万不要忘记@Controller @Controller @RequestMapping public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @RequestMapping(value = "/test" ,method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public Object test(){ return studentService.findAll(); } } 将项目打包File->Project Structure->Artifacts image-20230507162236159图片 如果有出现部分包不完全可以下图操作 image-20230507162342826图片 修改Tomcat配置(已正确安装Tomcat的情况下) image-20230507162648849图片 image-20230507162740440图片 启动Tomcat后在浏览器中访问localhost:8080/test 不报错有返回值,说明Spring整合SpringMVC配置成功。 image-20230507163245993图片
SSM开发环境搭建(小白自用) 前言 将SSM作为后端的的一个项目即将完工,在开发过程中踩了很多坑,与此同时也学习到了新知识,有了不小收获。在遇到麻烦和解决麻烦的路上,受到了很多分享教程博主的帮助。为了将帮助延续下去,我也将自己SSM环境配置的过程做了简单的纪录、分享。 系统软件版本 Windows 10 专业版 22H2 IntelliJ IDEA 2022.3.3 MySQL 8.0.32 Java 19.0.2 Spring 6.0.6 MyBatis 3.5.13 Tomcat 11.0.0 (软件系统版本不用完全一致,不同版本之间可能会出现一定程度的兼容性问题,可在有问题时在寻找对应版本的解决办法) 新建项目及项目配置 新建项目 使用IDEA新建一个空的默认Maven项目,并新建Java包完善SSM项目架构。 在新建controller包(表现层)、dao包(持久层)、service包(业务层) 在resources下新建db(存放数据库相关配置文件)、log(存放日志相关配置文件)、spring(存放与spring与其他整合相关配置文件) image-20230507141558542图片 修改Maven配置文件 使用默认Maven配置文件,在下载包时会比较慢,我们可以修改配置文件使用国内镜像来加速下载 IDEA内修改路径为File->Settings->Builde,Execution,Deployment->Maven 可以修改默认的文件,也可以重新使用一个自定义的配置文件,笔者这里使用了重新新建一个配置文件的方法。 image-20230507142114670图片 其中settings.xml文件中内容如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: | | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml | | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven | users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven | installation). It's normally provided in | ${maven.conf}/settings.xml. | | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: | | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml | | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. | |--> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.2.0.xsd"> <!-- localRepository | The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts. | | Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository <localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository> --> <!-- interactiveMode | This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, | maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for | the parameter in question. | | Default: true <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> --> <!-- offline | Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. | This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. | | Default: false <offline>false</offline> --> <!-- pluginGroups | This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e. | when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers | "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list. |--> <pluginGroups> <!-- pluginGroup | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> --> </pluginGroups> <!-- proxies | This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. | Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy | specification in this list marked as active will be used. |--> <proxies> <!-- proxy | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. | <proxy> <id>optional</id> <active>true</active> <protocol>http</protocol> <username>proxyuser</username> <password>proxypass</password> <host>proxy.host.net</host> <port>80</port> <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> </proxy> --> </proxies> <!-- servers | This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. | Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. |--> <servers> <!-- server | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by | a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below). | | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are | used together. | <server> <id>deploymentRepo</id> <username>repouser</username> <password>repopwd</password> </server> --> <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. <server> <id>siteServer</id> <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> </server> --> </servers> <!-- mirrors | This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories. | | It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts. | However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored | it to several places. | | That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that | repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred | server for that repository. |--> <mirrors> <!-- mirror | Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that | this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used | for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors. | <mirror> <id>mirrorId</id> <mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf> <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> <url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url> </mirror> --> <mirror> <id>aliment</id> <name>aliyah maven</name> <url>https://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> <mirror> <id>uk</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> <url>https://uk.maven.org/maven2/</url> </mirror> <mirror> <id>CN</id> <name>OSChina Central</name> <url>https://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> <mirror> <id>nexus</id> <name>internal nexus repository</name> <!-- <url>http://192.168.1.100:8081/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>--> <url>https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror> </mirrors> <!-- profiles | This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify | the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- | specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. | | For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where | your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is | dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin. | | As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles | section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially | relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property, | or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a | value of '1.4' might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of '1.4.2_07'. | Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line. | | NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact | repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration | variables for plugins in the POM. | |--> <profiles> <!-- profile | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. | | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention | for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc. | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug. | | This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo. <profile> <id>jdk-1.4</id> <activation> <jdk>1.4</jdk> </activation> <repositories> <repository> <id>jdk14</id> <name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name> <url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url> <layout>default</layout> <snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy> </repository> </repositories> </profile> --> <!-- | Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev', | which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration | might hypothetically look like: | | ... | <plugin> | <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId> | <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId> | | <configuration> | <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation> | </configuration> | </plugin> | ... | | NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to | anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property. | <profile> <id>env-dev</id> <activation> <property> <name>target-env</name> <value>dev</value> </property> </activation> <properties> <tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath> </properties> </profile> --> </profiles> <!-- activeProfiles | List of profiles that are active for all builds. | <activeProfiles> <activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> <activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> </activeProfiles> --> </settings> 只是修改了mirrors部分,使用了阿里云镜像加速国内下载速度。 设置项目所需包 修改pom.xml文件,以下内容为本人使用成功的配置文件内容,仅作参考 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.mango</groupId> <artifactId>ssmTest</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <!-- 工程编译版本,一般与安装的JDK版本一致--> <maven.compiler.source>19</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>19</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <!--统一的版本管理--> <spring.version>6.0.6</spring.version> <slf4j.version>2.0.5</slf4j.version> <mysql.version>8.0.32</mysql.version> <mybatis.version>3.5.13</mybatis.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.19</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!--Junit--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <!--数据库驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${mysql.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>c3p0</groupId> <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> <version>0.9.1.2</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <!--Servlet - JSP --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>jstl</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <!-- @Resource注解依赖包--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <!--Mybatis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>${mybatis.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring整合ORM --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>6.0.6</version> </dependency> <!-- spring整合mybatis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>3.0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- log --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>2.20.0</version> <type>pom</type> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <!--加入对json转换--> <!-- JSON: jackson --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.jr</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-jr-all</artifactId> <version>2.14.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>2.0.25</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.2.16</version> </dependency> <!-- http请求--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> <version>3.0.4</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> </resource> </resources> </build> </project> 添加Web模块 File->Project Structure->Modules 如图操作 image-20230507143328815图片 添加后内容保持默认,确认后即可导入web模块 安装Tomcat 可以参考以下教程 {% link Wxy1122.,[IntelliJ IDEA中配置Tomcat(超详细)_idea配置tomcat_Wxy1122.的博客-CSDN博客,https://blog.csdn.net/Wxy971122/article/details/123508532 %} SSM配置文件 jdbc配置文件 在resources->db下新建jdbc.properties文件,其中内容参考如下 jdbc.driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = root由于使用的MySQL版本为8,所以驱动才使用为com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,由于没有在MySQL中做过测试,不能确定在MySQL 5中也能正常使用 jdbc.url中的xxx用自己数据库名称替换 新建mybatis控制文件 在db下新建mybatis.xml文件 由于大部分和MyBatis相关配置文件都会和Spring的配置文件整合到一起,这里的Mybatis控制文件只起到辅助作用,参考代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 开启延迟加载 该项默认为false,即所有关联属性都会在初始化时加载 true表示延迟按需加载 --> <settings> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 开启二级缓存 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings> </configuration> Spring整合MyBatis 在resources->spring下新建applicationContext.xml文件,将Spring和MyBatis配置文件整合在一起,参考代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!-- 开启注解扫描,要扫描的是service和dao层的注解,要忽略web层注解,因为web层让SpringMVC框架去管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango"> <!-- 配置要忽略的注解 --> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> <!-- 引入配置文件 --> <bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:db/jdbc.properties" /> </bean> <!--Spring整合Mybatisl框架--> <!-- 配置C3P0的连接池对象 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置SessionFactory的Bean --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- 注入数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 指定MyBatis配置文件的位置 --> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:db/mybatis.xml"/> <!-- 给实体类起别名 --> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.mango.entity"/> </bean> <!-- 配置mapper接口的扫描器,将Mapper接口的实现类自动注入到IoC容器中 实现类Bean的名称默认为接口类名的首字母小写 --> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <!-- basePackage属性指定自动扫描mapper接口所在的包 --> <property name="basePackage" value="com.mango.dao"/> </bean> <!--SqlMapConfig.xml和jdbcConfig.properties可以删除了--> <!--配置Spring框架声明式事务管理--> <!--配置事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务的通知 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="*" isolation="DEFAULT"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置AOP增强 --> <aop:config> <!-- <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.mango.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>--> <!-- 配置切入点表达式 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.mango.service.impl.*.*(..))" id="pt1"/> <!-- 建立通知和切入点表达式的关系 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"/> </aop:config> </beans> Springmvc配置文件 在resources->spring下新建springmvc.xml文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 配置@controller扫描包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango.controller" /> <!--使用Annotation自动注册Bean,扫描@Controller和@ControllerAdvice--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mango" use-default-filters="false"> <!-- base-package 如果多个,用“,”分隔 --> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> <!--控制器增强,使一个Controller成为全局的异常处理类,类中用@ExceptionHandler方法注解的方法可以处理所有Controller发生的异常--> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice" /> </context:component-scan> <!-- 配置注解驱动,相当于同时使用最新处理器映射跟处理器适配器,对json数据响应提供支持 --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <!-- 输出对象转JSON支持 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="messageConverters"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"> <property name="supportedMediaTypes"> <list> <value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>text/plain;charset=UTF-8</value> <value>application/json;charset=UTF-8</value> </list> </property> </bean> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans> web模块控制文件 编辑web->WEB-INF->web.xml文件,内容如下 <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <!-- 配置前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- 指定配置文件位置和名称 如果不设置,默认找/WEB-INF/<servlet-name>-servlet.xml --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- 配置 spring 提供的监听器,用于启动服务时加载容器 。 该监听器只能加载 WEB-INF 目录中名称为 applicationContext.xml 的配置文件 --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 手动指定 spring 配置文件位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> </web-app> 日志配置 在resources->log下新建log4j.properties log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p %d %C: %m%n log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=INFO log4j.logger.org.apache=INFO log4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG 测试 在test->java下更具需求新建测试类 新建测试数据库test,其中有表student(id,name,age) 在之前新建的entity包中新建Student的实现类(getter、setter方法以省略) package com.mango.entity; public class Student { private int id; private String name; private String age; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age='" + age + '\'' + '}'; } } 对Spring和MyBatis整合配置测试 在包dao中新建学生接口StudentDao.java package com.mango.dao; import com.mango.entity.Student; import java.util.List; public interface StudentDao { public List<Student> findAll(); }在同样位置新建同名mapper文件StudentDao.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--命名空间为StudentDao接口--> <mapper namespace="com.mango.dao.StudentDao"> <!-- id为接口中的方法名--> <select id="findAll">SELECT * FROM Student</select> </mapper>在service包中新建service接口和实现类 image-20230507154913975图片 学生业务层接口StudentService.java package com.mango.service; import com.mango.entity.Student; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; //千万不要忘记添加Service注解 @Service public interface StudentService { public List<Student> findAll(); }实现类StudentServiceImpl.java package com.mango.service.impl; import com.mango.dao.StudentDao; import com.mango.entity.Student; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; public List<Student> findAll(){ return studentDao.findAll(); } }在test中新建Spring和MyBatis整合测试代码SpringMyBatis.java import com.mango.entity.Student; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml") public class SpringMyBatis { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @Test public void test(){ List<Student> studentList=studentService.findAll(); for (Student student:studentList){ System.out.println(student.toString()); } } } image-20230507161529932图片 测试成功 Spring整合SpringMVC测试 在Controller包中新建StudentController.java package com.mango.controller; import com.mango.service.StudentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; //千万不要忘记@Controller @Controller @RequestMapping public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @RequestMapping(value = "/test" ,method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public Object test(){ return studentService.findAll(); } } 将项目打包File->Project Structure->Artifacts image-20230507162236159图片 如果有出现部分包不完全可以下图操作 image-20230507162342826图片 修改Tomcat配置(已正确安装Tomcat的情况下) image-20230507162648849图片 image-20230507162740440图片 启动Tomcat后在浏览器中访问localhost:8080/test 不报错有返回值,说明Spring整合SpringMVC配置成功。 image-20230507163245993图片 -
 ESP32通过SmartConfig扫码配网 前引 对于ESP配网方式和SmartConfig的介绍,在ESP-IDF编程指南中已经介绍得很详细了,这里就不在赘述。 {% link ESP配网API,ESPRESSIF,https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/latest/esp32/api-reference/provisioning/index.html %} 这里主要来介绍一下在Arduino中怎么使用SmartConfig来实现微信扫码配网,配网失败的一些解决办法,主要代码参考了CSDN上的一篇文章(不能确定是不是原作者,对贡献代码的人都表示感谢) {% link ESP8266/ESP32 SmartConfig一键配网+自动重连+微信扫码配网,lw1997的博客-CSDN博客_esp32蓝牙配网,https://blog.csdn.net/u014091490/article/details/105178037 %} 正文 我只是在代码的原基础上做了简单的添加,指定了SmartConfig的Type #include "WiFi.h" void SmartConfig() { WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP_STA); Serial.println("\r\nWait for Smartconfig..."); WiFi.beginSmartConfig(SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH_AIRKISS); //我做了修改的部分添加了“SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH_AIRKISS” while (1) { Serial.print("."); delay(500); // wait for a second if (WiFi.smartConfigDone()) { Serial.println("SmartConfig Success"); Serial.printf("SSID:%s\r\n", WiFi.SSID().c_str()); Serial.printf("PSW:%s\r\n", WiFi.psk().c_str()); break; } } } bool AutoConfig() { WiFi.begin(); //如果觉得时间太长可改 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { int wstatus = WiFi.status(); if (wstatus == WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.println("WIFI SmartConfig Success"); Serial.printf("SSID:%s", WiFi.SSID().c_str()); Serial.printf(", PSW:%s\r\n", WiFi.psk().c_str()); Serial.print("LocalIP:"); Serial.print(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.print(" ,GateIP:"); Serial.println(WiFi.gatewayIP()); return true; } else { Serial.print("WIFI AutoConfig Waiting......"); Serial.println(wstatus); delay(1000); } } Serial.println("WIFI AutoConfig Faild!" ); return false; } void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); delay(100); if (!AutoConfig()) { SmartConfig(); } } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: }在使用作者源代码的时候,微信扫码和ESPTouch APP都没有成功,然后看到说要指定连接的类型,就可以解决 image-20230205231815105图片 根据自己的需求选合适的类型就行。 关于连接工具 微信扫码 官方给的工具网址为:https://iot.espressif.cn/configWXDeviceWiFi.html 可以利用网址链接转二维码工具生成二维码,像我生成的二维码: QRcode_SP — 2图片 利用ESPTouch 可以到ESP官网下载软件,有Android和iOS版本 {% link 资源 | 乐鑫科技,ESPRESSIF,https://www.espressif.com.cn/zh-hans/products/software/esp-touch/resources %} 乐鑫信息科技微信公众号 image-20230205235550535图片 image-20230205235507900图片
ESP32通过SmartConfig扫码配网 前引 对于ESP配网方式和SmartConfig的介绍,在ESP-IDF编程指南中已经介绍得很详细了,这里就不在赘述。 {% link ESP配网API,ESPRESSIF,https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/zh_CN/latest/esp32/api-reference/provisioning/index.html %} 这里主要来介绍一下在Arduino中怎么使用SmartConfig来实现微信扫码配网,配网失败的一些解决办法,主要代码参考了CSDN上的一篇文章(不能确定是不是原作者,对贡献代码的人都表示感谢) {% link ESP8266/ESP32 SmartConfig一键配网+自动重连+微信扫码配网,lw1997的博客-CSDN博客_esp32蓝牙配网,https://blog.csdn.net/u014091490/article/details/105178037 %} 正文 我只是在代码的原基础上做了简单的添加,指定了SmartConfig的Type #include "WiFi.h" void SmartConfig() { WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP_STA); Serial.println("\r\nWait for Smartconfig..."); WiFi.beginSmartConfig(SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH_AIRKISS); //我做了修改的部分添加了“SC_TYPE_ESPTOUCH_AIRKISS” while (1) { Serial.print("."); delay(500); // wait for a second if (WiFi.smartConfigDone()) { Serial.println("SmartConfig Success"); Serial.printf("SSID:%s\r\n", WiFi.SSID().c_str()); Serial.printf("PSW:%s\r\n", WiFi.psk().c_str()); break; } } } bool AutoConfig() { WiFi.begin(); //如果觉得时间太长可改 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { int wstatus = WiFi.status(); if (wstatus == WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.println("WIFI SmartConfig Success"); Serial.printf("SSID:%s", WiFi.SSID().c_str()); Serial.printf(", PSW:%s\r\n", WiFi.psk().c_str()); Serial.print("LocalIP:"); Serial.print(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.print(" ,GateIP:"); Serial.println(WiFi.gatewayIP()); return true; } else { Serial.print("WIFI AutoConfig Waiting......"); Serial.println(wstatus); delay(1000); } } Serial.println("WIFI AutoConfig Faild!" ); return false; } void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); delay(100); if (!AutoConfig()) { SmartConfig(); } } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: }在使用作者源代码的时候,微信扫码和ESPTouch APP都没有成功,然后看到说要指定连接的类型,就可以解决 image-20230205231815105图片 根据自己的需求选合适的类型就行。 关于连接工具 微信扫码 官方给的工具网址为:https://iot.espressif.cn/configWXDeviceWiFi.html 可以利用网址链接转二维码工具生成二维码,像我生成的二维码: QRcode_SP — 2图片 利用ESPTouch 可以到ESP官网下载软件,有Android和iOS版本 {% link 资源 | 乐鑫科技,ESPRESSIF,https://www.espressif.com.cn/zh-hans/products/software/esp-touch/resources %} 乐鑫信息科技微信公众号 image-20230205235550535图片 image-20230205235507900图片 -
 饥荒联机服务器搭建(本地、云服务器、双云服务器) 前引 饥荒联机是一个制作精良的“多人联机”生存游戏,游戏在可玩性上没得说,但是由于房主PC性能和网络等各种不确定性原因,导致联机体验特别糟糕。 猎杀时刻图片 对于联机卡顿的情况,可以通过搭建饥荒联机服务器来解决。 我会比较详细的介绍饥荒联机服务器搭建的过程,其中包括本地服务器搭建、云服务器搭建、通过两个服务器将地面和洞穴世界分开服务器搭建 KLEI服务器访问令牌 无论搭建什么类型的服务器此步骤都不能省略,获取到后可以暂时保存到记事本中,后面会用到 进入游戏 打开饥荒联机版,进入菜单界面 点击账号 image-20230131212932263图片 找到饥荒服务器 在导航栏中选择 游戏 ,找到饥荒联机版的图标,选择《饥荒:联机版》的游戏服务器 image-20230131213355872图片 添加服务器 名字可以随便取,取好名字之后就可以添加服务器 image-20230131213945834图片 获取代码 其他的都不用配置,直接复制访问令牌就可以 image-20230131214244181图片 创建新世界 根据自己的喜好创建一个新的饥荒世界,配置好人数,世界属性,以及添加需要的服务器模组之后就和平时玩一样创建一个新世界。 在选人界面直接退出 image-20230131220545275图片 找到新世界存档,位置一般在C:\Users\mstzf\Documents\Klei\DoNotStarveTogether文件夹下面的那个数字文件夹里面存放着不同世界的文件夹。文件以Cluster_1来命名,找到新创建的世界文件夹点击进入。 在文件中添加新文件,命名为cluster_token.txt,一定要注意扩展名为. txt如果默认不显示扩展名的要注意可能会出错。打开 cluster_token.txt 将上一步获取的服务器访问令牌粘贴在里面保存退出。 image-20230131224430759图片 根据需求修改添加,其中必须要在默认的基础上加入 cluster_tooken.txt才可以搭建联机服务器 Cavers :饥荒联机版洞穴世界配置文件。 Master :饥荒联机版主世界配置文件。 adminlist.txt :管理员名单,在文件中写入玩家的KLEI ID可以将玩家变为服务器管理员,拥有控制台输入命令和踢人的权限。 blocklist.txt :黑名单,加入KLEI ID的玩家无法加入游戏。 cluster.ini :饥荒联机版配置文件,可以设置人数和世界模式等,可根据需要修改。 whitelist.txt :服务器白名单,可写入玩家KLEI ID加入白名单,服务器会空出白名单人数的可加入人数。如果服务器可以有人,白名单中有一人,那么如果白名单中的人不在世界中的话,实际可加入的人数就只有5人。 做完这些,这个游戏存档就可以被做为饥荒的联机服务器存档了 饥荒本地联机服务器搭建 复制存档 将之前配置的游戏存档复制到他的上一级C:\Users\mstzf\Documents\Klei\DoNotStarveTogether中 下载饥荒联机工具 打开Steam游戏库,将游戏软件那个下拉箭头中,将工具也勾上 image-20230131224118410图片 在目录中找到Don't Starve Together Dedicated Server,并下载安装 image-20230131224631734图片 编辑启动文件 通过Steam直接打开服务器本地文件(也可以通过文件夹打开,路径为:Steam安装位置\steamapps\common\Don't Starve Together Dedicated Server image-20230131230145959图片 找到 bin/scripts/launch_preconfigured_servers.bat 文件 修改launch_preconfigured_servers.bat文件内容为 @ECHO OFF set SteamAppId=322330 set SteamGameId=322330 cd .. start "Don't Starve Together Overworld" /D "%~dp0.." "%~dp0..\dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer.exe" -cluster 改为新建世界存档名 -console -shard Master -console start "Don't Starve Together Caves" /D "%~dp0.." "%~dp0..\dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer.exe" -cluster 改为新建世界存档名 -console -shard Caves -console如果你的服务器不需要任何服务器mod,那么可以直接点击launch_preconfigured_servers.bat文件启动服务器 添加mod 对于本地搭建服务器的mod,可以直接复制原本饥荒的mod文件夹中的mod文件到饥荒服务器文件夹中的mod文件夹中 找饥荒联机版文件的方法和之前一样,这里就不在赘述 image-20230131233553886图片 另一种方法时编辑mod文件夹下面的dedicated_server_mods_setup.lua ServerModSetup("350811795") --数字为mod的id号 ServerModCollectionSetup("379114180") --数字为合计的id号对于怎么获取mod和合集的id,可以在Steam的创意工坊中,在mod或者合集订阅页面复制网页URL,在获取的网址中的数字就是mod或者合集的id号 云服务器搭建 饥荒联机云服务器相比与本地,有更好的网络连接条件,我本人在用一个2核2G的云服务器,短期档10人左右基本不卡,长期档6人以内也可以支持。 对于服务器的话,如果是学生,可以在阿里云进行学生认证,有着不错的折扣。 {% link 阿里云学生优惠链接,阿里云,https://www.aliyun.com/daily-act/ecs/activity_share?userCode=6vfvkhtz %} 我的环境是Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS 安装依赖环境 更新系统 sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y安装依赖环境 sudo apt-get install lib32gcc1 libstdc++6 libgcc1 libcurl4-gnutls-dev -y 创建Steam安装目录 mkdir ~/Steam cd Steam 下载SteamCMD安装软件 wget https://steamcdn-a.akamaihd.net/client/installer/steamcmd_linux.tar.gz等待下载完成 对软件解压缩 tar -zxvf steamcmd_linux.tar.gz 运行SteamCMD ./steamcmd.sh当看到Steam> 就说明安装配置已经成功 最有可能出现问题的就是在安装依赖的时候,多根据报错检查 image-20230201172759557图片 指定游戏安装路径 我喜欢装在Steam文件夹下,可以根据自己喜好修改 force_install_dir /root/Steam/DSTServer 登录Steam下载饥荒服务器 login anonymous app_update 343050 validate等待游戏下载完成 image-20230201173810519图片 完成后可以使用Ctrl + C 或者输入quit 退出SteamCMD 编辑启动脚本 可以通过直接运行文件来启动服务器 ./root/Steam/DSTServer/bin/dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer 但是这样不方便管理 在启动时如果出现报错: error while loading shared libraries: libcurl-gnutls.so.4: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 或者 error while loading shared libraries: libstdc++.so.6: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 这里是个大坑。是由于缺少对应的库,开启i386支持再去安装对应的库 开启i386支持 sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 更新软件库 sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y 安装缺少的库 sudo apt install libcurl4-gnutls-dev:i386 sudo apt install libstdc++6:i386启动脚本可以被放在任何位置,我习惯放在root下自建的bash文件下 mkdir /root/bash cd /root/bash vim startDST.sh没有vim的可以用:sudo apt install vim -y 安装 启动脚本: steamcmd_dir为steamcmd.sh路径 install_dir 为游戏安装路径 cluster_name为存档名 #!/bin/bash steamcmd_dir="/root/Steam" install_dir="/root/Steam/DSTServer" cluster_name="Cluster_1" dontstarve_dir="/root/.klei/DoNotStarveTogether" function fail() { echo Error: "$@" >&2 exit 1 } function check_for_file() { if [ ! -e "$1" ]; then fail "Missing file: $1" fi } cd "$steamcmd_dir" || fail "Missing $steamcmd_dir directory!" check_for_file "steamcmd.sh" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/cluster.ini" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/cluster_token.txt" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/Master/server.ini" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/Caves/server.ini" check_for_file "$install_dir/bin" cd "$install_dir/bin" || fail run_shared=(./dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer) run_shared+=(-console) run_shared+=(-cluster "$cluster_name") run_shared+=(-monitor_parent_process $$) run_shared+=(-shard) "${run_shared[@]}" Caves | sed 's/^/Caves: /' & "${run_shared[@]}" Master | sed 's/^/Master: /' 给脚本文件可执行权限 sudo chmod u+x /root/bash/startDST.sh执行脚本用 :./root/bash/startDST.sh 添加mod vim /root/Steam/DSTserver/mods/dedicated_server_mods_setup.lua编辑文件内容 ServerModCollectionSetup("2606822598") -- 括号内数字替换为自己需要订阅的合集id ServerModSetup("1505270912") -- 括号内数字替换为自己需要订阅的mod的idimage-20230201183857430图片 上传世界存档文件夹 上传服务器的方式有很多 软件方式可以使用FileZilla {% link ,FileZilla中文网 - 免费开源的FTP解决方案,FileZilla,https://www.filezilla.cn %} 上传到服务器后将文件夹保存到:/root/.klei/DoNotStarveTogether/下面,并修改启动脚本中cluster_name的值 找不到文件夹的可以先./root/Steam/DSTServer/bin/dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer运行一下 完成后就可以运行启动脚本,启动饥荒联机服务器 后台运行 推荐使用screen 下载 sudo apt install screen -y 启动 screen -S DST 关闭 Ctrl+A+D 双服务器分开地面和洞穴 要带一些大型模组的多人长期档,一个性能低的服务器可能无法满足,此时如果有多个服务器可以采用不同服务器跑不同部分的办法实现。 要使用这一方法,需要在每个服务器都安装饥荒服务器环境,并且都要上传饥荒游戏存档。 主要要编辑洞穴服务器的cluster.ini文件 image-20230202021547548图片 对于启动文件,只需要将最后的两部分根据需要注释掉就可以了 如果是主世界的启动程序就注释带有Caves的那一行,如果是洞穴就注释带有Master的那一行,然后要保证主世界先运行起来再启动洞穴 image-20230202021920313图片
饥荒联机服务器搭建(本地、云服务器、双云服务器) 前引 饥荒联机是一个制作精良的“多人联机”生存游戏,游戏在可玩性上没得说,但是由于房主PC性能和网络等各种不确定性原因,导致联机体验特别糟糕。 猎杀时刻图片 对于联机卡顿的情况,可以通过搭建饥荒联机服务器来解决。 我会比较详细的介绍饥荒联机服务器搭建的过程,其中包括本地服务器搭建、云服务器搭建、通过两个服务器将地面和洞穴世界分开服务器搭建 KLEI服务器访问令牌 无论搭建什么类型的服务器此步骤都不能省略,获取到后可以暂时保存到记事本中,后面会用到 进入游戏 打开饥荒联机版,进入菜单界面 点击账号 image-20230131212932263图片 找到饥荒服务器 在导航栏中选择 游戏 ,找到饥荒联机版的图标,选择《饥荒:联机版》的游戏服务器 image-20230131213355872图片 添加服务器 名字可以随便取,取好名字之后就可以添加服务器 image-20230131213945834图片 获取代码 其他的都不用配置,直接复制访问令牌就可以 image-20230131214244181图片 创建新世界 根据自己的喜好创建一个新的饥荒世界,配置好人数,世界属性,以及添加需要的服务器模组之后就和平时玩一样创建一个新世界。 在选人界面直接退出 image-20230131220545275图片 找到新世界存档,位置一般在C:\Users\mstzf\Documents\Klei\DoNotStarveTogether文件夹下面的那个数字文件夹里面存放着不同世界的文件夹。文件以Cluster_1来命名,找到新创建的世界文件夹点击进入。 在文件中添加新文件,命名为cluster_token.txt,一定要注意扩展名为. txt如果默认不显示扩展名的要注意可能会出错。打开 cluster_token.txt 将上一步获取的服务器访问令牌粘贴在里面保存退出。 image-20230131224430759图片 根据需求修改添加,其中必须要在默认的基础上加入 cluster_tooken.txt才可以搭建联机服务器 Cavers :饥荒联机版洞穴世界配置文件。 Master :饥荒联机版主世界配置文件。 adminlist.txt :管理员名单,在文件中写入玩家的KLEI ID可以将玩家变为服务器管理员,拥有控制台输入命令和踢人的权限。 blocklist.txt :黑名单,加入KLEI ID的玩家无法加入游戏。 cluster.ini :饥荒联机版配置文件,可以设置人数和世界模式等,可根据需要修改。 whitelist.txt :服务器白名单,可写入玩家KLEI ID加入白名单,服务器会空出白名单人数的可加入人数。如果服务器可以有人,白名单中有一人,那么如果白名单中的人不在世界中的话,实际可加入的人数就只有5人。 做完这些,这个游戏存档就可以被做为饥荒的联机服务器存档了 饥荒本地联机服务器搭建 复制存档 将之前配置的游戏存档复制到他的上一级C:\Users\mstzf\Documents\Klei\DoNotStarveTogether中 下载饥荒联机工具 打开Steam游戏库,将游戏软件那个下拉箭头中,将工具也勾上 image-20230131224118410图片 在目录中找到Don't Starve Together Dedicated Server,并下载安装 image-20230131224631734图片 编辑启动文件 通过Steam直接打开服务器本地文件(也可以通过文件夹打开,路径为:Steam安装位置\steamapps\common\Don't Starve Together Dedicated Server image-20230131230145959图片 找到 bin/scripts/launch_preconfigured_servers.bat 文件 修改launch_preconfigured_servers.bat文件内容为 @ECHO OFF set SteamAppId=322330 set SteamGameId=322330 cd .. start "Don't Starve Together Overworld" /D "%~dp0.." "%~dp0..\dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer.exe" -cluster 改为新建世界存档名 -console -shard Master -console start "Don't Starve Together Caves" /D "%~dp0.." "%~dp0..\dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer.exe" -cluster 改为新建世界存档名 -console -shard Caves -console如果你的服务器不需要任何服务器mod,那么可以直接点击launch_preconfigured_servers.bat文件启动服务器 添加mod 对于本地搭建服务器的mod,可以直接复制原本饥荒的mod文件夹中的mod文件到饥荒服务器文件夹中的mod文件夹中 找饥荒联机版文件的方法和之前一样,这里就不在赘述 image-20230131233553886图片 另一种方法时编辑mod文件夹下面的dedicated_server_mods_setup.lua ServerModSetup("350811795") --数字为mod的id号 ServerModCollectionSetup("379114180") --数字为合计的id号对于怎么获取mod和合集的id,可以在Steam的创意工坊中,在mod或者合集订阅页面复制网页URL,在获取的网址中的数字就是mod或者合集的id号 云服务器搭建 饥荒联机云服务器相比与本地,有更好的网络连接条件,我本人在用一个2核2G的云服务器,短期档10人左右基本不卡,长期档6人以内也可以支持。 对于服务器的话,如果是学生,可以在阿里云进行学生认证,有着不错的折扣。 {% link 阿里云学生优惠链接,阿里云,https://www.aliyun.com/daily-act/ecs/activity_share?userCode=6vfvkhtz %} 我的环境是Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS 安装依赖环境 更新系统 sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y安装依赖环境 sudo apt-get install lib32gcc1 libstdc++6 libgcc1 libcurl4-gnutls-dev -y 创建Steam安装目录 mkdir ~/Steam cd Steam 下载SteamCMD安装软件 wget https://steamcdn-a.akamaihd.net/client/installer/steamcmd_linux.tar.gz等待下载完成 对软件解压缩 tar -zxvf steamcmd_linux.tar.gz 运行SteamCMD ./steamcmd.sh当看到Steam> 就说明安装配置已经成功 最有可能出现问题的就是在安装依赖的时候,多根据报错检查 image-20230201172759557图片 指定游戏安装路径 我喜欢装在Steam文件夹下,可以根据自己喜好修改 force_install_dir /root/Steam/DSTServer 登录Steam下载饥荒服务器 login anonymous app_update 343050 validate等待游戏下载完成 image-20230201173810519图片 完成后可以使用Ctrl + C 或者输入quit 退出SteamCMD 编辑启动脚本 可以通过直接运行文件来启动服务器 ./root/Steam/DSTServer/bin/dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer 但是这样不方便管理 在启动时如果出现报错: error while loading shared libraries: libcurl-gnutls.so.4: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 或者 error while loading shared libraries: libstdc++.so.6: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 这里是个大坑。是由于缺少对应的库,开启i386支持再去安装对应的库 开启i386支持 sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 更新软件库 sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y 安装缺少的库 sudo apt install libcurl4-gnutls-dev:i386 sudo apt install libstdc++6:i386启动脚本可以被放在任何位置,我习惯放在root下自建的bash文件下 mkdir /root/bash cd /root/bash vim startDST.sh没有vim的可以用:sudo apt install vim -y 安装 启动脚本: steamcmd_dir为steamcmd.sh路径 install_dir 为游戏安装路径 cluster_name为存档名 #!/bin/bash steamcmd_dir="/root/Steam" install_dir="/root/Steam/DSTServer" cluster_name="Cluster_1" dontstarve_dir="/root/.klei/DoNotStarveTogether" function fail() { echo Error: "$@" >&2 exit 1 } function check_for_file() { if [ ! -e "$1" ]; then fail "Missing file: $1" fi } cd "$steamcmd_dir" || fail "Missing $steamcmd_dir directory!" check_for_file "steamcmd.sh" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/cluster.ini" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/cluster_token.txt" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/Master/server.ini" check_for_file "$dontstarve_dir/$cluster_name/Caves/server.ini" check_for_file "$install_dir/bin" cd "$install_dir/bin" || fail run_shared=(./dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer) run_shared+=(-console) run_shared+=(-cluster "$cluster_name") run_shared+=(-monitor_parent_process $$) run_shared+=(-shard) "${run_shared[@]}" Caves | sed 's/^/Caves: /' & "${run_shared[@]}" Master | sed 's/^/Master: /' 给脚本文件可执行权限 sudo chmod u+x /root/bash/startDST.sh执行脚本用 :./root/bash/startDST.sh 添加mod vim /root/Steam/DSTserver/mods/dedicated_server_mods_setup.lua编辑文件内容 ServerModCollectionSetup("2606822598") -- 括号内数字替换为自己需要订阅的合集id ServerModSetup("1505270912") -- 括号内数字替换为自己需要订阅的mod的idimage-20230201183857430图片 上传世界存档文件夹 上传服务器的方式有很多 软件方式可以使用FileZilla {% link ,FileZilla中文网 - 免费开源的FTP解决方案,FileZilla,https://www.filezilla.cn %} 上传到服务器后将文件夹保存到:/root/.klei/DoNotStarveTogether/下面,并修改启动脚本中cluster_name的值 找不到文件夹的可以先./root/Steam/DSTServer/bin/dontstarve_dedicated_server_nullrenderer运行一下 完成后就可以运行启动脚本,启动饥荒联机服务器 后台运行 推荐使用screen 下载 sudo apt install screen -y 启动 screen -S DST 关闭 Ctrl+A+D 双服务器分开地面和洞穴 要带一些大型模组的多人长期档,一个性能低的服务器可能无法满足,此时如果有多个服务器可以采用不同服务器跑不同部分的办法实现。 要使用这一方法,需要在每个服务器都安装饥荒服务器环境,并且都要上传饥荒游戏存档。 主要要编辑洞穴服务器的cluster.ini文件 image-20230202021547548图片 对于启动文件,只需要将最后的两部分根据需要注释掉就可以了 如果是主世界的启动程序就注释带有Caves的那一行,如果是洞穴就注释带有Master的那一行,然后要保证主世界先运行起来再启动洞穴 image-20230202021920313图片 -
 树莓派烧录系统不再折腾 把树莓派作为路由器之后,很长一段时间都没有再折腾树莓派上的东西。最近准备用树莓派做一个人脸识别的系统,就去树莓派官网 准备下载个新的系统,树莓派的官方烧录软件居然更新了。 在之前的版本中,界面是英文的、而且只能对TF卡格式化和烧录系统,在没有桌面显示器的情况下安装新系统有很多地方要折腾,开启SSH,添加默认WiFi链接... image-20220614193852774图片 在1.7版本中,界面已经可以支持中文,最主要的还是在系统烧录时可以配置wifi、用户名、是否开启SSH、语言... image-20220614195504459图片 右下加的设置图片可以对烧录后的系统进行设置 image-20220614201506953图片 虽然烧录系统很简单,配置起来也可以直接在网上找到很多教程,但是谁能拒绝如此方便的配置过程呢
树莓派烧录系统不再折腾 把树莓派作为路由器之后,很长一段时间都没有再折腾树莓派上的东西。最近准备用树莓派做一个人脸识别的系统,就去树莓派官网 准备下载个新的系统,树莓派的官方烧录软件居然更新了。 在之前的版本中,界面是英文的、而且只能对TF卡格式化和烧录系统,在没有桌面显示器的情况下安装新系统有很多地方要折腾,开启SSH,添加默认WiFi链接... image-20220614193852774图片 在1.7版本中,界面已经可以支持中文,最主要的还是在系统烧录时可以配置wifi、用户名、是否开启SSH、语言... image-20220614195504459图片 右下加的设置图片可以对烧录后的系统进行设置 image-20220614201506953图片 虽然烧录系统很简单,配置起来也可以直接在网上找到很多教程,但是谁能拒绝如此方便的配置过程呢